In the contemporary digital landscape, the demand for seamless user experiences is at an unprecedented level. Offline-first applications have emerged as a crucial solution, enabling users to engage with content without the limitations imposed by internet connectivity, ensuring seamless user engagement. This approach not only enhances accessibility but also significantly improves overall user satisfaction. However, the development of these applications presents a unique set of challenges. This discussion will delve into the importance of offline-first apps, their benefits, the challenges developers encounter, and best practices for successful implementation. It is essential to understand why the offline-first approach represents the future of app development.
The Importance of Offline-First Apps in Mobile Applications
The emergence of offline-first applications is significantly transforming the mobile application landscape by prioritizing user experience and functionality, even in the absence of consistent network connectivity.
As businesses adapt to technological trends that emphasize accessibility and user-centric design, offline-first applications have become vital for ensuring uninterrupted usability and effective data synchronization, a key aspect of digital transformation.
This approach not only enhances user engagement but also aligns with the increasing demand for mobile usability and operational efficiency in today’s competitive app development environment.
Why Offline-First Apps are Gaining Popularity in the Rise of Mobile-First Approach
Offline-first applications are experiencing a surge in popularity due to their capacity to align with user preferences and enhance retention by providing seamless offline functionality and immediate access to content.
This trend is predominantly fueled by the increasing reliance on mobile applications, as consumers increasingly seek solutions that operate effectively regardless of internet connectivity. Users frequently encounter environments with poor or unstable connections, rendering offline capabilities essential for a smooth user experience.
The rising demand for uninterrupted user experiences across various sectors, including education and retail, highlights the strategic value of these applications. As developers emphasize offline-first design, they are addressing market demand that not only enhances user engagement but also promotes longer retention periods, thereby further solidifying the appeal of these innovative tools.
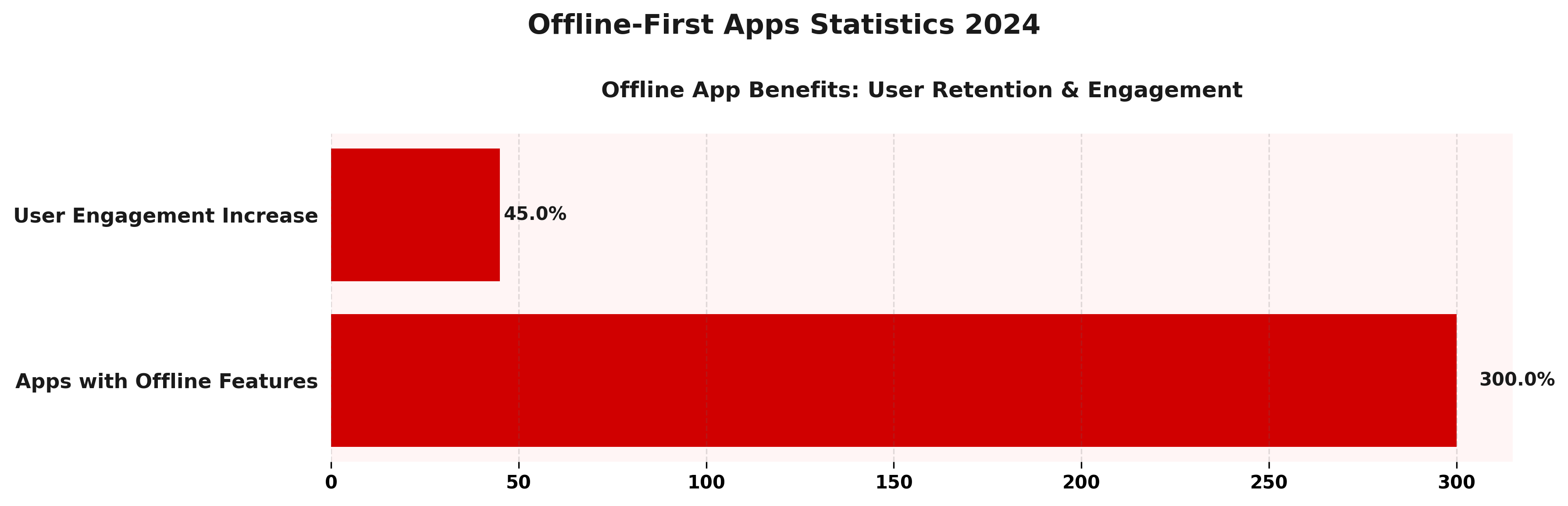
Offline-First Apps Statistics 2024
Explore the app performance metrics through this infographic.
The Offline-First Apps Statistics 2024 provides insights into the advantages of integrating offline features into mobile applications. It focuses on how these features impact user retention and engagement, leveraging technology to offer uninterrupted service irrespective of connectivity.
Offline App Benefits underscore the significant potential of offline features in enhancing app performance. Notably, 300% of apps have adopted offline features, reflecting the robust trend towards maintaining functionality without constant internet access. This adoption is crucial for users in areas with unstable connectivity or those who travel frequently, ensuring that the app remains functional and useful.
- User Retention and Engagement: These offline features contribute to a substantial 45% increase in user engagement, highlighting their importance in user retention strategies.
The commitment to offline functionality in apps indicates a shift in developer focus towards user-centric design, prioritizing accessibility and reliability. This evolution not only benefits users but also fosters loyalty and satisfaction, as apps that ‘always work’ win favor among users. In competitive markets, the ability to offer uninterrupted service can be a decisive factor in user preference, illustrating the importance of offline capabilities in modern app development.
Benefits of Offline-First Apps in Enhancing Usability and Customer Satisfaction
The advantages of offline-first applications extend well beyond fundamental functionality. They notably enhance user experience and accessibility, ensuring that users can depend on offline capabilities for uninterrupted service.
Improved User Experience and Accessibility
Improved user experience and accessibility are key advantages of offline-first applications, as they eliminate barriers associated with limited internet connectivity and ensure consistent user engagement, contributing to customer satisfaction and user empowerment.
By enabling users to access essential features and content without the necessity of a constant internet connection, these applications facilitate seamless interactions that enhance user satisfaction. When mobile usability is prioritized, individuals can navigate complex tasks and access critical information with ease, irrespective of their environment.
This approach not only strengthens engagement strategies by encouraging users to interact with the application at any time, but it also promotes inclusivity.
Users situated in areas with unstable connections or those with limited data plans derive significant benefits from the reliable performance of offline functionality, ultimately contributing to an overall enriched user experience.
Challenges and Solutions for Offline-First Development in Cross-Platform Applications
The offline-first development approach presents numerous advantages; however, it also introduces several challenges that developers must address.
Among these challenges are connectivity issues and data storage concerns, which must be effectively managed to ensure optimal application performance.
Addressing Connectivity and Data Storage Issues with Effective Caching Strategies
Addressing connectivity and data storage issues is essential for maintaining offline capabilities and ensuring application resilience, which in turn fosters user trust in the app’s reliability.
To achieve this, a multi-faceted approach may be employed. Implementing robust caching strategies can significantly reduce reliance on constant connectivity by storing essential data locally for immediate access, crucial for offline access and real-time syncing.
Additionally, adopting cloud-based solutions enhances data redundancy and facilitates seamless synchronization once connectivity is restored. Regularly updating backend systems to manage data efficiently is critical to ensuring that users experience minimal interruptions, even in challenging connectivity scenarios.
Incorporating user feedback can further refine these strategies, ensuring that the application aligns with user needs and expectations. This approach ultimately reinforces user trust in the platform’s capability to function effectively, irrespective of network conditions.
Best Practices for Creating Offline-First Apps in Ensuring Reliability and Latency Reduction
Implementing best practices for the development of offline-first applications is crucial for optimizing their effectiveness. This includes designing applications with offline usage in mind and ensuring efficient data synchronization across the mobile ecosystem.
Designing for Offline Usage and Syncing in Progressive Web Apps
Designing applications for offline usage and effective synchronization is essential for creating user-centric solutions that prioritize performance optimization and provide a seamless user interface experience.
This approach not only enhances the overall functionality of the application but also ensures users can access their data at any time and from any location, independent of a constant internet connection, bolstering the mobile user experience.
Key considerations include the development of intuitive navigation elements that facilitate straightforward offline interaction, as well as ensuring the application retains crucial features even in situations of limited connectivity.
The implementation of intelligent caching strategies and background synchronization techniques can significantly enhance performance, allowing for efficient data updates once connectivity is restored.
By concentrating on these critical aspects, developers can create robust applications that effectively meet user needs, even in challenging connectivity scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions About Offline-First Philosophy
What are offline-first apps and why are they becoming more important?
Offline-first apps are applications that are designed to function even without an internet connection. They are becoming more important because of the growing reliance on mobile devices and the need for uninterrupted access to information and services.
How do offline-first apps work and Enhance User Journeys?
Offline-first apps store data on the device and use it to provide a seamless user experience even when there is no internet connection. Any changes made while offline are synced with the server once a connection is available again.
What are the benefits of using offline-first apps in Digital Well-being?
Offline-first apps offer several benefits, including improved user experience, increased productivity, and reduced reliance on internet connectivity. They also provide a more efficient use of data and can save on data costs.
Are offline-first apps only useful for areas with poor internet connectivity?
No, offline-first apps are useful in any situation where there may be unreliable or limited internet access. They can also be beneficial for users who travel frequently or have limited data plans.
How are offline-first apps impacting the tech industry and Technology Trends?
The rise of offline-first apps is pushing the tech industry to develop more efficient and effective solutions for offline functionality, leveraging service workers and native apps for enhanced offline mode and network independence. It is also changing the way businesses approach web and app development, placing a greater emphasis on offline capabilities, application security, and resource efficiency, driven by changing consumer behavior and technology adoption.
What are some examples of successful offline-first apps that showcase innovation and competitive advantage?
Some popular offline-first apps include Google Maps, Evernote, and Pocket, which demonstrate responsive design, cloud integration, and app ecosystems. These apps allow users to access and use their features even when offline, providing a seamless experience, feature parity, and application lifecycle management while optimizing data usage and download speed.






Comments closed.